- Sri Lanka
-
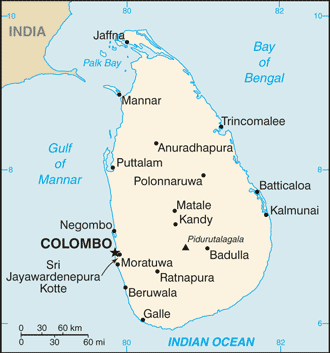 Introduction ::Sri LankaBackground:The first Sinhalese arrived in Sri Lanka late in the 6th century B.C., probably from northern India. Buddhism was introduced in about the mid-third century B.C., and a great civilization developed at the cities of Anuradhapura (kingdom from circa 200 B.C. to circa A.D. 1000) and Polonnaruwa (from about 1070 to 1200). In the 14th century, a south Indian dynasty established a Tamil kingdom in northern Sri Lanka. The coastal areas of the island were controlled by the Portuguese in the 16th century and by the Dutch in the 17th century. The island was ceded to the British in 1796, became a crown colony in 1802, and was formally united under British rule by 1815. As Ceylon, it became independent in 1948; its name was changed to Sri Lanka in 1972. Tensions between the Sinhalese majority and Tamil separatists erupted into war in 1983. After two decades of fighting, the government and Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) formalized a cease-fire in February 2002 with Norway brokering peace negotiations. Violence between the LTTE and government forces intensified in 2006, but the government regained control of the Eastern Province in 2007. By May 2009, the government announced that its military had defeated the remnants of the LTTE. Since the end of the conflict, the government has enacted an ambitious program of economic development projects, many of which are financed by loans from the Government of China. In addition to efforts to reconstruct its economy, the government has resettled more than 95% of those civilians who were displaced during the final phase of the conflict and released the vast majority of former LTTE combatants captured by Government Security Forces. At the same time, there has been little progress on more contentious and politically difficult issues such as reaching a political settlement with Tamil elected representatives and holding accountable those alleged to have been involved in human rights violations at the end of the war.Geography ::Sri LankaLocation:Southern Asia, island in the Indian Ocean, south of IndiaGeographic coordinates:7 00 N, 81 00 EArea:total: 65,610 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 122land: 64,630 sq kmwater: 980 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly larger than West VirginiaLand boundaries:0 kmCoastline:1,340 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental marginClimate:tropical monsoon; northeast monsoon (December to March); southwest monsoon (June to October)Terrain:mostly low, flat to rolling plain; mountains in south-central interiorElevation extremes:lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 mhighest point: Pidurutalagala 2,524 mNatural resources:limestone, graphite, mineral sands, gems, phosphates, clay, hydropowerLand use:arable land: 18.29%permanent crops: 14.94%other: 66.77% (2011)Irrigated land:5,700 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:52.8 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 12.95 cu km/yr (6%/6%/87%)per capita: 638.8 cu m/yr (2005)Natural hazards:occasional cyclones and tornadoesEnvironment - current issues:deforestation; soil erosion; wildlife populations threatened by poaching and urbanization; coastal degradation from mining activities and increased pollution; freshwater resources being polluted by industrial wastes and sewage runoff; waste disposal; air pollution in ColomboEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: Marine Life ConservationGeography - note:strategic location near major Indian Ocean sea lanesPeople and Society ::Sri LankaNationality:noun: Sri Lankan(s)adjective: Sri LankanEthnic groups:Sinhalese 73.8%, Sri Lankan Moors 7.2%, Indian Tamil 4.6%, Sri Lankan Tamil 3.9%, other 0.5%, unspecified 10% (2001 census provisional data)Languages:Sinhala (official and national language) 74%, Tamil (national language) 18%, other 8%note: English, spoken competently by about 10% of the population, is commonly used in government and is referred to as the link language in the constitutionReligions:Buddhist (official) 69.1%, Muslim 7.6%, Hindu 7.1%, Christian 6.2%, unspecified 10% (2001 census provisional data)Population:21,675,648 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Age structure:0-14 years: 24.8% (male 2,741,879/female 2,632,613)15-24 years: 15.1% (male 1,659,566/female 1,615,616)25-54 years: 42.4% (male 4,484,738/female 4,697,355)55-64 years: 9.3% (male 939,174/female 1,084,108)65 years and over: 8.4% (male 778,629/female 1,041,970) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 50.7 %youth dependency ratio: 37.9 %elderly dependency ratio: 12.8 %potential support ratio: 7.8 (2013)Median age:total: 31.4 yearsmale: 30.3 yearsfemale: 32.5 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:0.89% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 126Birth rate:16.64 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Death rate:6.01 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 162Net migration rate:-1.74 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 157Urbanization:urban population: 15.1% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 1.36% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:COLOMBO (capital) 681,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.95 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.87 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:22.6note: Median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2000 est.)Maternal mortality rate:35 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 119Infant mortality rate:total: 9.24 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 147male: 10.21 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 8.24 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 76.15 yearscountry comparison to the world: 83male: 72.64 yearsfemale: 79.79 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:2.15 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 107Contraceptive prevalence rate:68% (2006/07)Health expenditures:3% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 179Physicians density:0.49 physicians/1,000 population (2006)Hospital bed density:3.1 beds/1,000 population (2004)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 99% of populationrural: 90% of populationtotal: 91% of populationunimproved:urban: 1% of populationrural: 10% of populationtotal: 9% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 88% of populationrural: 93% of populationtotal: 92% of populationunimproved:urban: 12% of populationrural: 7% of populationtotal: 8% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:less than 0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 132HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:2,800 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 129HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 200 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 102Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis Avectorborne disease: dengue feverwater contact disease: leptospirosisanimal contact disease: rabies (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:5.1% (2008)country comparison to the world: 155Children under the age of 5 years underweight:21.6% (2009)country comparison to the world: 27Education expenditures:2% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 166Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 91.2%male: 92.6%female: 90% (2010 census)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 14 yearsmale: 14 yearsfemale: 14 years (2011)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 19.4%country comparison to the world: 61male: 16.3%female: 24.7% (2010)Government ::Sri LankaCountry name:conventional long form: Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lankaconventional short form: Sri Lankalocal long form: Shri Lanka Prajatantrika Samajavadi Janarajaya/Ilankai Jananayaka Choshalichak Kutiyarachulocal short form: Shri Lanka/Ilankaiformer: Serendib, CeylonGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Colombogeographic coordinates: 6 55 N, 79 50 Etime difference: UTC+5.5 (10.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)note: Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte (legislative capital)Administrative divisions:9 provinces; Central, Eastern, North Central, Northern, North Western, Sabaragamuwa, Southern, Uva, WesternIndependence:4 February 1948 (from the UK)National holiday:Independence Day, 4 February (1948)Constitution:adopted 16 August 1978, certified 31 August 1978; amended many times, most recently in 2010Legal system:mixed legal system of Roman-Dutch civil law, English common law, and Jaffna Tamil customary lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Mahinda Percy RAJAPAKSA (since 19 November 2005); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government; Dissanayake Mudiyanselage JAYARATNE holds the largely ceremonial title of prime minister (since 21 April 2010)head of government: President Mahinda Percy RAJAPAKSA (since 19 November 2005)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president in consultation with the prime minister(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a six-year term, eligible for a second term; election last held on 26 January 2010 (next to be held in 2016)election results: Mahinda Percy RAJAPAKSA reelected president for second term; percent of vote - Mahinda Percy RAJAPAKSA 57.88%, Sarath FONSEKA 40.15%, other 1.97%Legislative branch:unicameral Parliament (225 seats; members elected by popular vote on the basis of an open-list, proportional representation system by electoral district to serve six-year terms)elections: last held on 8 April 2010 with a repoll in two electorates held on 20 April 2010 (next to be held by April 2016)election results: percent of vote by alliance or party - United People's Freedom Alliance 60.93%, United National Party 29.34%, Democratic National Alliance 5.49%, Tamil National Alliance 2.9%, other 1.34%; seats by alliance or party - United People's Freedom Alliance 144, United National Party 60, Tamil National Alliance 14, Democratic National Alliance 7Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court of the Republic (consists of the chief justice and 10 justices); note - the court has exclusive jurisdiction to review legislationjudge selection and term of office: the chief justice appointed by the president; the other justices appointed by the president with the advice of the chief justice; all justices hold office until age 65subordinate courts: Court of Appeals; High Courts; Magistrate's Courts; municipal and primary courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Coalitions and leaders: Democratic National Alliance, led by General (Retired) Sarath FONSEKAJanatha Vimukthi Peramuna or JVP [Somawansa AMARASINGHE]Tamil National Alliance led by Illandai Tamil Arasu Kachchi [R. SAMPANTHAN]United National Front led by United National Party [Ranil WICKREMESINGHE]United People's Freedom Alliance led by Sri Lanka Freedom Party [Mahinda RAJAPAKSA]Political pressure groups and leaders:Buddhist clergylabor unionshard-line nationalist Sinhalese groups such as the National Movement Against TerrorismSinhalese Buddhist lay groupsInternational organization participation:ABEDA, ADB, ARF, BIMSTEC, C, CD, CP, FAO, G-11, G-15, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, SAARC, SACEP, SCO (dialogue member), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Jaliya Chitran WICKRAMASURIYAchancery: 2148 Wyoming Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 483-4025 through 4028FAX: [1] (202) 232-7181consulate(s) general: Los Angelesconsulate(s): New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Michele J. SISONembassy: 210 Galle Road, Colombo 3mailing address: P. O. Box 106, Colombotelephone: [94] (11) 249-8500FAX: [94] (11) 243-7345Flag description:yellow with two panels; the smaller hoist-side panel has two equal vertical bands of green (hoist side) and orange; the other larger panel depicts a yellow lion holding a sword on a dark red rectangular field that also displays a yellow bo leaf in each corner; the yellow field appears as a border around the entire flag and extends between the two panels; the lion represents Sinhalese ethnicity, the strength of the nation, and bravery; the sword demonstrates the sovereignty of the nation; the four bo leaves - symbolizing Buddhism and its influence on the country - stand for the four virtues of kindness, friendliness, happiness, and equanimity; orange signifies Sri Lankan Tamils, green the Sri Lankan Moors; dark red represents the European Burghers, but also refers to the rich colonial background of the country; yellow denotes other ethnic groups; also referred to as the Lion FlagNational symbol(s):lionNational anthem:name: ""Sri Lanka Matha"" (Mother Sri Lanka)lyrics/music: Ananda SAMARKONEnote: adopted 1951Economy ::Sri LankaEconomy - overview:Sri Lanka continues to experience strong economic growth following the end of the 26-year conflict with the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE). The government has been pursuing large-scale reconstruction and development projects in its efforts to spur growth in war-torn and disadvantaged areas, develop small and medium enterprises and increase agricultural productivity. The government's high debt payments and bloated civil service have contributed to historically high budget deficits, but fiscal consolidation efforts and strong GDP growth in recent years have helped bring down the government's fiscal deficit. However, low tax revenues are a major concern. The 2008-09 global financial crisis and recession exposed Sri Lanka''s economic vulnerabilities and nearly caused a balance of payments crisis. Growth slowed to 3.5% in 2009. Economic activity rebounded with the end of the war and an IMF agreement, resulting in two straight years of 8% growth in 2010-11. Growth moderated to about 6% in 2012. Agriculture slowed due to a drought and weak global demand affected exports and trade. In early 2012, Sri Lanka floated the rupee, resulting in a sharp depreciation, and took steps to curb imports. A large trade deficit remains a concern. Strong remittances from Sri Lankan workers abroad have helped to offset the trade deficit.GDP (purchasing power parity):$128.4 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 67$120.6 billion (2011 est.)$111.4 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$59.41 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:6.4% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 378.2% (2011 est.)8% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$6,200 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 146$5,900 (2011 est.)$5,500 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:23.8% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 5322.1% of GDP (2011 est.)25.3% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 69.6%government consumption: 13.5%investment in fixed capital: 28.9%investment in inventories: 1.8%exports of goods and services: 22.8%imports of goods and services: -36.5%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 11.1%industry: 31.5%services: 57.5% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:rice, sugarcane, grains, pulses, oilseed, spices, vegetables, fruit, tea, rubber, coconuts; milk, eggs, hides, beef; fishIndustries:processing of rubber, tea, coconuts, tobacco and other agricultural commodities; telecommunications, insurance, banking; tourism, shipping; clothing, textiles; cement, petroleum refining, information technology services, constructionIndustrial production growth rate:10.3% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9Labor force:8.194 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 58Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 31.8%industry: 25.8%services: 42.4% (June 2012)Unemployment rate:5.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 474.2% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:8.9% (2010 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 1.6%highest 10%: 39.5% (2009)Distribution of family income - Gini index:49 (2010)country comparison to the world: 2446 (1995)Budget:revenues: $7.868 billionexpenditures: $11.63 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:13.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-6.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 183Public debt:77.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 3078.4% of GDP (2011 est.)note: covers central government debt, and excludes debt instruments directly owned by government entities other than the treasury (e.g. commercial bank borrowings of a government corporation); the data includes treasury debt held by foreign entities as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement; sub-national entities are usually not permitted to sell debt instrumentsFiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):7.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1826.7% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:7.5% (19 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 377% (31 December 2011 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:13.25% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 959.41% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$3.539 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 110$3.852 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$21.89 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 82$18.88 billion (31 December 2010 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$28.86 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 72$26.53 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$16.92 billion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 65$19.44 billion (31 December 2011)$19.92 billion (31 December 2010)Current account balance:-$4.737 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 164-$4.638 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$9.785 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 95$10.56 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:textiles and apparel, tea and spices; rubber manufactures; precious stones; coconut products, fishExports - partners:US 22.6%, UK 9.8%, India 6.4%, Belgium 5.2%, Germany 4.8%, Italy 4.3% (2012)Imports:$17.32 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 82$18.24 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:petroleum, textiles, machinery and transportation equipment, building materials, mineral products, foodstuffsImports - partners:India 21.3%, China 16.5%, Singapore 8.6%, Iran 7.7%, UAE 4.4%, Malaysia 4.3% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$6.831 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 83$6.748 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$26.87 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 76$23.98 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$NAStock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$NAExchange rates:Sri Lankan rupees (LKR) per US dollar -127.6 (2012 est.)110.57 (2011 est.)113.06 (2010 est.)114.95 (2009)108.33 (2008)Energy ::Sri LankaElectricity - production:11.52 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Electricity - consumption:10 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 89Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Electricity - installed generating capacity:3.139 million kW (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Electricity - from fossil fuels:53.8% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 147Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 61Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:44.6% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Electricity - from other renewable sources:1.6% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 117Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Crude oil - imports:41,000 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 115Refined petroleum products - production:50,000 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 84Refined petroleum products - consumption:89,620 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 162Refined petroleum products - imports:48,140 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 111Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 127Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 172Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:14.09 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 90Communications ::Sri LankaTelephones - main lines in use:2.832 million (2013)country comparison to the world: 52Telephones - mobile cellular:19.336 million (2013)country comparison to the world: 49Telephone system:general assessment: telephone services have improved significantly and are available in most parts of the countrydomestic: national trunk network consists mostly of digital microwave radio relay; fiber-optic links now in use in Colombo area and fixed wireless local loops have been installed; competition is strong in mobile cellular systems and mobile cellular subscribership is increasinginternational: country code - 94; the SEA-ME-WE-3 and SEA-ME-WE-4 submarine cables provide connectivity to Asia, Australia, Middle East, Europe, US; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) (2011)Broadcast media:government operates 8 TV channels and a radio network; multi-channel satellite and cable TV subscription services available; 35 private TV stations and about 50 radio stations (2012)Internet country code:.lkInternet hosts:9,552 (2012)country comparison to the world: 136Internet users:1.777 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 77Transportation ::Sri LankaAirports:19 (2013)country comparison to the world: 138Airports - with paved runways:total: 15over 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 6914 to 1,523 m: 7 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 4914 to 1,523 m: 1under 914 m:3 (2013)Heliports:1 (2013)Railways:total: 1,449 kmcountry comparison to the world: 80broad gauge: 1,449 km 1.676-m gauge (2007)Roadways:total: 91,907 km (2008)country comparison to the world: 51Waterways:160 km (primarily on rivers in southwest) (2012)country comparison to the world: 101Merchant marine:total: 21country comparison to the world: 94by type: bulk carrier 4, cargo 13, chemical tanker 1, container 1, petroleum tanker 2foreign-owned: 8 (Germany 8) (2010)Ports and terminals:ColomboMilitary ::Sri LankaMilitary branches:Sri Lanka Army, Sri Lanka Navy, Sri Lanka Air Force (2013)Military service age and obligation:18-22 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; 5-year service obligation (Air Force) (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 5,342,147females age 16-49: 5,466,409 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 4,177,432females age 16-49: 4,574,833 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 167,026female: 162,587 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:2.9% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 42Transnational Issues ::Sri LankaDisputes - international:noneRefugees and internally displaced persons:IDPs: 118,376 (civil war; more than half displaced prior to 2008; many of the more than 470,000 IDPs registered as returnees had not reached durable solutions as of September 2012) (2012)Trafficking in persons:current situation: Sri Lanka is primarily a source and, to a much lesser extent, a destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; some Sri Lankan adults and children who migrate willingly to Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Bahrain, Lebanon, Iraq, Afghanistan, Malaysia, and Singapore to work as domestic servants, construction workers, or garment factory workers face conditions indicative of forced labor; some Sri Lankan women are forced into prostitution in Jordan, Singapore, Maldives, and other countries; within Sri Lanka, women and children are subjected to sex trafficking in brothels, while other children are forced to work in the agriculture, fireworks, and fish-drying industriestier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Sri Lanka does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; law enforcement efforts and victim protection, particularly identification, are very weak, with no reported prosecutions or convictions under the country's penal code article prohibiting human trafficking; government employees' complicity in trafficking offenses remains a problem; the government has not approved its draft standard operating procedures for identifying trafficking victims and referring them to protective services, consequently, victims may have been punished for crimes committed as a direct result of being trafficked; the government adopted an anti-trafficking action plan in 2012 (2013)"
Introduction ::Sri LankaBackground:The first Sinhalese arrived in Sri Lanka late in the 6th century B.C., probably from northern India. Buddhism was introduced in about the mid-third century B.C., and a great civilization developed at the cities of Anuradhapura (kingdom from circa 200 B.C. to circa A.D. 1000) and Polonnaruwa (from about 1070 to 1200). In the 14th century, a south Indian dynasty established a Tamil kingdom in northern Sri Lanka. The coastal areas of the island were controlled by the Portuguese in the 16th century and by the Dutch in the 17th century. The island was ceded to the British in 1796, became a crown colony in 1802, and was formally united under British rule by 1815. As Ceylon, it became independent in 1948; its name was changed to Sri Lanka in 1972. Tensions between the Sinhalese majority and Tamil separatists erupted into war in 1983. After two decades of fighting, the government and Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) formalized a cease-fire in February 2002 with Norway brokering peace negotiations. Violence between the LTTE and government forces intensified in 2006, but the government regained control of the Eastern Province in 2007. By May 2009, the government announced that its military had defeated the remnants of the LTTE. Since the end of the conflict, the government has enacted an ambitious program of economic development projects, many of which are financed by loans from the Government of China. In addition to efforts to reconstruct its economy, the government has resettled more than 95% of those civilians who were displaced during the final phase of the conflict and released the vast majority of former LTTE combatants captured by Government Security Forces. At the same time, there has been little progress on more contentious and politically difficult issues such as reaching a political settlement with Tamil elected representatives and holding accountable those alleged to have been involved in human rights violations at the end of the war.Geography ::Sri LankaLocation:Southern Asia, island in the Indian Ocean, south of IndiaGeographic coordinates:7 00 N, 81 00 EArea:total: 65,610 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 122land: 64,630 sq kmwater: 980 sq kmArea - comparative:slightly larger than West VirginiaLand boundaries:0 kmCoastline:1,340 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental marginClimate:tropical monsoon; northeast monsoon (December to March); southwest monsoon (June to October)Terrain:mostly low, flat to rolling plain; mountains in south-central interiorElevation extremes:lowest point: Indian Ocean 0 mhighest point: Pidurutalagala 2,524 mNatural resources:limestone, graphite, mineral sands, gems, phosphates, clay, hydropowerLand use:arable land: 18.29%permanent crops: 14.94%other: 66.77% (2011)Irrigated land:5,700 sq km (2003)Total renewable water resources:52.8 cu km (2011)Freshwater withdrawal (domestic/industrial/agricultural):total: 12.95 cu km/yr (6%/6%/87%)per capita: 638.8 cu m/yr (2005)Natural hazards:occasional cyclones and tornadoesEnvironment - current issues:deforestation; soil erosion; wildlife populations threatened by poaching and urbanization; coastal degradation from mining activities and increased pollution; freshwater resources being polluted by industrial wastes and sewage runoff; waste disposal; air pollution in ColomboEnvironment - international agreements:party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: Marine Life ConservationGeography - note:strategic location near major Indian Ocean sea lanesPeople and Society ::Sri LankaNationality:noun: Sri Lankan(s)adjective: Sri LankanEthnic groups:Sinhalese 73.8%, Sri Lankan Moors 7.2%, Indian Tamil 4.6%, Sri Lankan Tamil 3.9%, other 0.5%, unspecified 10% (2001 census provisional data)Languages:Sinhala (official and national language) 74%, Tamil (national language) 18%, other 8%note: English, spoken competently by about 10% of the population, is commonly used in government and is referred to as the link language in the constitutionReligions:Buddhist (official) 69.1%, Muslim 7.6%, Hindu 7.1%, Christian 6.2%, unspecified 10% (2001 census provisional data)Population:21,675,648 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 57Age structure:0-14 years: 24.8% (male 2,741,879/female 2,632,613)15-24 years: 15.1% (male 1,659,566/female 1,615,616)25-54 years: 42.4% (male 4,484,738/female 4,697,355)55-64 years: 9.3% (male 939,174/female 1,084,108)65 years and over: 8.4% (male 778,629/female 1,041,970) (2013 est.)Dependency ratios:total dependency ratio: 50.7 %youth dependency ratio: 37.9 %elderly dependency ratio: 12.8 %potential support ratio: 7.8 (2013)Median age:total: 31.4 yearsmale: 30.3 yearsfemale: 32.5 years (2013 est.)Population growth rate:0.89% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 126Birth rate:16.64 births/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Death rate:6.01 deaths/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 162Net migration rate:-1.74 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 157Urbanization:urban population: 15.1% of total population (2011)rate of urbanization: 1.36% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Major urban areas - population:COLOMBO (capital) 681,000 (2009)Sex ratio:at birth: 1.04 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.04 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.95 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.87 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.75 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.96 male(s)/female (2013 est.)Mother's mean age at first birth:22.6note: Median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2000 est.)Maternal mortality rate:35 deaths/100,000 live births (2010)country comparison to the world: 119Infant mortality rate:total: 9.24 deaths/1,000 live birthscountry comparison to the world: 147male: 10.21 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 8.24 deaths/1,000 live births (2013 est.)Life expectancy at birth:total population: 76.15 yearscountry comparison to the world: 83male: 72.64 yearsfemale: 79.79 years (2013 est.)Total fertility rate:2.15 children born/woman (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 107Contraceptive prevalence rate:68% (2006/07)Health expenditures:3% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 179Physicians density:0.49 physicians/1,000 population (2006)Hospital bed density:3.1 beds/1,000 population (2004)Drinking water source:improved:urban: 99% of populationrural: 90% of populationtotal: 91% of populationunimproved:urban: 1% of populationrural: 10% of populationtotal: 9% of population (2010 est.)Sanitation facility access:improved:urban: 88% of populationrural: 93% of populationtotal: 92% of populationunimproved:urban: 12% of populationrural: 7% of populationtotal: 8% of population (2010 est.)HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:less than 0.1% (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 132HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:2,800 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 129HIV/AIDS - deaths:fewer than 200 (2009 est.)country comparison to the world: 102Major infectious diseases:degree of risk: highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea and hepatitis Avectorborne disease: dengue feverwater contact disease: leptospirosisanimal contact disease: rabies (2013)Obesity - adult prevalence rate:5.1% (2008)country comparison to the world: 155Children under the age of 5 years underweight:21.6% (2009)country comparison to the world: 27Education expenditures:2% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 166Literacy:definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 91.2%male: 92.6%female: 90% (2010 census)School life expectancy (primary to tertiary education):total: 14 yearsmale: 14 yearsfemale: 14 years (2011)Unemployment, youth ages 15-24:total: 19.4%country comparison to the world: 61male: 16.3%female: 24.7% (2010)Government ::Sri LankaCountry name:conventional long form: Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lankaconventional short form: Sri Lankalocal long form: Shri Lanka Prajatantrika Samajavadi Janarajaya/Ilankai Jananayaka Choshalichak Kutiyarachulocal short form: Shri Lanka/Ilankaiformer: Serendib, CeylonGovernment type:republicCapital:name: Colombogeographic coordinates: 6 55 N, 79 50 Etime difference: UTC+5.5 (10.5 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)note: Sri Jayewardenepura Kotte (legislative capital)Administrative divisions:9 provinces; Central, Eastern, North Central, Northern, North Western, Sabaragamuwa, Southern, Uva, WesternIndependence:4 February 1948 (from the UK)National holiday:Independence Day, 4 February (1948)Constitution:adopted 16 August 1978, certified 31 August 1978; amended many times, most recently in 2010Legal system:mixed legal system of Roman-Dutch civil law, English common law, and Jaffna Tamil customary lawInternational law organization participation:has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCtSuffrage:18 years of age; universalExecutive branch:chief of state: President Mahinda Percy RAJAPAKSA (since 19 November 2005); note - the president is both the chief of state and head of government; Dissanayake Mudiyanselage JAYARATNE holds the largely ceremonial title of prime minister (since 21 April 2010)head of government: President Mahinda Percy RAJAPAKSA (since 19 November 2005)cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president in consultation with the prime minister(For more information visit the World Leaders website )elections: president elected by popular vote for a six-year term, eligible for a second term; election last held on 26 January 2010 (next to be held in 2016)election results: Mahinda Percy RAJAPAKSA reelected president for second term; percent of vote - Mahinda Percy RAJAPAKSA 57.88%, Sarath FONSEKA 40.15%, other 1.97%Legislative branch:unicameral Parliament (225 seats; members elected by popular vote on the basis of an open-list, proportional representation system by electoral district to serve six-year terms)elections: last held on 8 April 2010 with a repoll in two electorates held on 20 April 2010 (next to be held by April 2016)election results: percent of vote by alliance or party - United People's Freedom Alliance 60.93%, United National Party 29.34%, Democratic National Alliance 5.49%, Tamil National Alliance 2.9%, other 1.34%; seats by alliance or party - United People's Freedom Alliance 144, United National Party 60, Tamil National Alliance 14, Democratic National Alliance 7Judicial branch:highest court(s): Supreme Court of the Republic (consists of the chief justice and 10 justices); note - the court has exclusive jurisdiction to review legislationjudge selection and term of office: the chief justice appointed by the president; the other justices appointed by the president with the advice of the chief justice; all justices hold office until age 65subordinate courts: Court of Appeals; High Courts; Magistrate's Courts; municipal and primary courtsPolitical parties and leaders:Coalitions and leaders: Democratic National Alliance, led by General (Retired) Sarath FONSEKAJanatha Vimukthi Peramuna or JVP [Somawansa AMARASINGHE]Tamil National Alliance led by Illandai Tamil Arasu Kachchi [R. SAMPANTHAN]United National Front led by United National Party [Ranil WICKREMESINGHE]United People's Freedom Alliance led by Sri Lanka Freedom Party [Mahinda RAJAPAKSA]Political pressure groups and leaders:Buddhist clergylabor unionshard-line nationalist Sinhalese groups such as the National Movement Against TerrorismSinhalese Buddhist lay groupsInternational organization participation:ABEDA, ADB, ARF, BIMSTEC, C, CD, CP, FAO, G-11, G-15, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSTAH, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS (observer), OPCW, PCA, SAARC, SACEP, SCO (dialogue member), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMISS, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTODiplomatic representation in the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Jaliya Chitran WICKRAMASURIYAchancery: 2148 Wyoming Avenue NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 483-4025 through 4028FAX: [1] (202) 232-7181consulate(s) general: Los Angelesconsulate(s): New YorkDiplomatic representation from the US:chief of mission: Ambassador Michele J. SISONembassy: 210 Galle Road, Colombo 3mailing address: P. O. Box 106, Colombotelephone: [94] (11) 249-8500FAX: [94] (11) 243-7345Flag description:yellow with two panels; the smaller hoist-side panel has two equal vertical bands of green (hoist side) and orange; the other larger panel depicts a yellow lion holding a sword on a dark red rectangular field that also displays a yellow bo leaf in each corner; the yellow field appears as a border around the entire flag and extends between the two panels; the lion represents Sinhalese ethnicity, the strength of the nation, and bravery; the sword demonstrates the sovereignty of the nation; the four bo leaves - symbolizing Buddhism and its influence on the country - stand for the four virtues of kindness, friendliness, happiness, and equanimity; orange signifies Sri Lankan Tamils, green the Sri Lankan Moors; dark red represents the European Burghers, but also refers to the rich colonial background of the country; yellow denotes other ethnic groups; also referred to as the Lion FlagNational symbol(s):lionNational anthem:name: ""Sri Lanka Matha"" (Mother Sri Lanka)lyrics/music: Ananda SAMARKONEnote: adopted 1951Economy ::Sri LankaEconomy - overview:Sri Lanka continues to experience strong economic growth following the end of the 26-year conflict with the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE). The government has been pursuing large-scale reconstruction and development projects in its efforts to spur growth in war-torn and disadvantaged areas, develop small and medium enterprises and increase agricultural productivity. The government's high debt payments and bloated civil service have contributed to historically high budget deficits, but fiscal consolidation efforts and strong GDP growth in recent years have helped bring down the government's fiscal deficit. However, low tax revenues are a major concern. The 2008-09 global financial crisis and recession exposed Sri Lanka''s economic vulnerabilities and nearly caused a balance of payments crisis. Growth slowed to 3.5% in 2009. Economic activity rebounded with the end of the war and an IMF agreement, resulting in two straight years of 8% growth in 2010-11. Growth moderated to about 6% in 2012. Agriculture slowed due to a drought and weak global demand affected exports and trade. In early 2012, Sri Lanka floated the rupee, resulting in a sharp depreciation, and took steps to curb imports. A large trade deficit remains a concern. Strong remittances from Sri Lankan workers abroad have helped to offset the trade deficit.GDP (purchasing power parity):$128.4 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 67$120.6 billion (2011 est.)$111.4 billion (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGDP (official exchange rate):$59.41 billion (2012 est.)GDP - real growth rate:6.4% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 378.2% (2011 est.)8% (2010 est.)GDP - per capita (PPP):$6,200 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 146$5,900 (2011 est.)$5,500 (2010 est.)note: data are in 2012 US dollarsGross national saving:23.8% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 5322.1% of GDP (2011 est.)25.3% of GDP (2010 est.)GDP - composition, by end use:household consumption: 69.6%government consumption: 13.5%investment in fixed capital: 28.9%investment in inventories: 1.8%exports of goods and services: 22.8%imports of goods and services: -36.5%(2012 est.)GDP - composition, by sector of origin:agriculture: 11.1%industry: 31.5%services: 57.5% (2012 est.)Agriculture - products:rice, sugarcane, grains, pulses, oilseed, spices, vegetables, fruit, tea, rubber, coconuts; milk, eggs, hides, beef; fishIndustries:processing of rubber, tea, coconuts, tobacco and other agricultural commodities; telecommunications, insurance, banking; tourism, shipping; clothing, textiles; cement, petroleum refining, information technology services, constructionIndustrial production growth rate:10.3% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 9Labor force:8.194 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 58Labor force - by occupation:agriculture: 31.8%industry: 25.8%services: 42.4% (June 2012)Unemployment rate:5.2% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 474.2% (2011 est.)Population below poverty line:8.9% (2010 est.)Household income or consumption by percentage share:lowest 10%: 1.6%highest 10%: 39.5% (2009)Distribution of family income - Gini index:49 (2010)country comparison to the world: 2446 (1995)Budget:revenues: $7.868 billionexpenditures: $11.63 billion (2012 est.)Taxes and other revenues:13.2% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 199Budget surplus (+) or deficit (-):-6.3% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 183Public debt:77.7% of GDP (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 3078.4% of GDP (2011 est.)note: covers central government debt, and excludes debt instruments directly owned by government entities other than the treasury (e.g. commercial bank borrowings of a government corporation); the data includes treasury debt held by foreign entities as well as intra-governmental debt; intra-governmental debt consists of treasury borrowings from surpluses in the social funds, such as for retirement; sub-national entities are usually not permitted to sell debt instrumentsFiscal year:calendar yearInflation rate (consumer prices):7.5% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1826.7% (2011 est.)Central bank discount rate:7.5% (19 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 377% (31 December 2011 est.)Commercial bank prime lending rate:13.25% (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 959.41% (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of narrow money:$3.539 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 110$3.852 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of broad money:$21.89 billion (31 December 2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 82$18.88 billion (31 December 2010 est.)Stock of domestic credit:$28.86 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 72$26.53 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Market value of publicly traded shares:$16.92 billion (31 December 2012)country comparison to the world: 65$19.44 billion (31 December 2011)$19.92 billion (31 December 2010)Current account balance:-$4.737 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 164-$4.638 billion (2011 est.)Exports:$9.785 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 95$10.56 billion (2011 est.)Exports - commodities:textiles and apparel, tea and spices; rubber manufactures; precious stones; coconut products, fishExports - partners:US 22.6%, UK 9.8%, India 6.4%, Belgium 5.2%, Germany 4.8%, Italy 4.3% (2012)Imports:$17.32 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 82$18.24 billion (2011 est.)Imports - commodities:petroleum, textiles, machinery and transportation equipment, building materials, mineral products, foodstuffsImports - partners:India 21.3%, China 16.5%, Singapore 8.6%, Iran 7.7%, UAE 4.4%, Malaysia 4.3% (2012)Reserves of foreign exchange and gold:$6.831 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 83$6.748 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Debt - external:$26.87 billion (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 76$23.98 billion (31 December 2011 est.)Stock of direct foreign investment - at home:$NAStock of direct foreign investment - abroad:$NAExchange rates:Sri Lankan rupees (LKR) per US dollar -127.6 (2012 est.)110.57 (2011 est.)113.06 (2010 est.)114.95 (2009)108.33 (2008)Energy ::Sri LankaElectricity - production:11.52 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 91Electricity - consumption:10 billion kWh (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 89Electricity - exports:0 kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 174Electricity - imports:0 kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 168Electricity - installed generating capacity:3.139 million kW (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 87Electricity - from fossil fuels:53.8% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 147Electricity - from nuclear fuels:0% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 61Electricity - from hydroelectric plants:44.6% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 49Electricity - from other renewable sources:1.6% of total installed capacity (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 65Crude oil - production:0 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 117Crude oil - exports:0 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 92Crude oil - imports:41,000 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 59Crude oil - proved reserves:0 bbl (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 115Refined petroleum products - production:50,000 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 84Refined petroleum products - consumption:89,620 bbl/day (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 81Refined petroleum products - exports:0 bbl/day (2008 est.)country comparison to the world: 162Refined petroleum products - imports:48,140 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 68Natural gas - production:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 111Natural gas - consumption:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 127Natural gas - exports:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 75Natural gas - imports:0 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 172Natural gas - proved reserves:0 cu m (1 January 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 120Carbon dioxide emissions from consumption of energy:14.09 million Mt (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 90Communications ::Sri LankaTelephones - main lines in use:2.832 million (2013)country comparison to the world: 52Telephones - mobile cellular:19.336 million (2013)country comparison to the world: 49Telephone system:general assessment: telephone services have improved significantly and are available in most parts of the countrydomestic: national trunk network consists mostly of digital microwave radio relay; fiber-optic links now in use in Colombo area and fixed wireless local loops have been installed; competition is strong in mobile cellular systems and mobile cellular subscribership is increasinginternational: country code - 94; the SEA-ME-WE-3 and SEA-ME-WE-4 submarine cables provide connectivity to Asia, Australia, Middle East, Europe, US; satellite earth stations - 2 Intelsat (Indian Ocean) (2011)Broadcast media:government operates 8 TV channels and a radio network; multi-channel satellite and cable TV subscription services available; 35 private TV stations and about 50 radio stations (2012)Internet country code:.lkInternet hosts:9,552 (2012)country comparison to the world: 136Internet users:1.777 million (2009)country comparison to the world: 77Transportation ::Sri LankaAirports:19 (2013)country comparison to the world: 138Airports - with paved runways:total: 15over 3,047 m: 21,524 to 2,437 m: 6914 to 1,523 m: 7 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 4914 to 1,523 m: 1under 914 m:3 (2013)Heliports:1 (2013)Railways:total: 1,449 kmcountry comparison to the world: 80broad gauge: 1,449 km 1.676-m gauge (2007)Roadways:total: 91,907 km (2008)country comparison to the world: 51Waterways:160 km (primarily on rivers in southwest) (2012)country comparison to the world: 101Merchant marine:total: 21country comparison to the world: 94by type: bulk carrier 4, cargo 13, chemical tanker 1, container 1, petroleum tanker 2foreign-owned: 8 (Germany 8) (2010)Ports and terminals:ColomboMilitary ::Sri LankaMilitary branches:Sri Lanka Army, Sri Lanka Navy, Sri Lanka Air Force (2013)Military service age and obligation:18-22 years of age for voluntary military service; no conscription; 5-year service obligation (Air Force) (2012)Manpower available for military service:males age 16-49: 5,342,147females age 16-49: 5,466,409 (2010 est.)Manpower fit for military service:males age 16-49: 4,177,432females age 16-49: 4,574,833 (2010 est.)Manpower reaching militarily significant age annually:male: 167,026female: 162,587 (2010 est.)Military expenditures:2.9% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 42Transnational Issues ::Sri LankaDisputes - international:noneRefugees and internally displaced persons:IDPs: 118,376 (civil war; more than half displaced prior to 2008; many of the more than 470,000 IDPs registered as returnees had not reached durable solutions as of September 2012) (2012)Trafficking in persons:current situation: Sri Lanka is primarily a source and, to a much lesser extent, a destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; some Sri Lankan adults and children who migrate willingly to Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Bahrain, Lebanon, Iraq, Afghanistan, Malaysia, and Singapore to work as domestic servants, construction workers, or garment factory workers face conditions indicative of forced labor; some Sri Lankan women are forced into prostitution in Jordan, Singapore, Maldives, and other countries; within Sri Lanka, women and children are subjected to sex trafficking in brothels, while other children are forced to work in the agriculture, fireworks, and fish-drying industriestier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Sri Lanka does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; law enforcement efforts and victim protection, particularly identification, are very weak, with no reported prosecutions or convictions under the country's penal code article prohibiting human trafficking; government employees' complicity in trafficking offenses remains a problem; the government has not approved its draft standard operating procedures for identifying trafficking victims and referring them to protective services, consequently, victims may have been punished for crimes committed as a direct result of being trafficked; the government adopted an anti-trafficking action plan in 2012 (2013)"
The World Factbook. 2014.
